NORTH AMERICA
Crystal D.
Foundations to 600 CE
Native American Groups:
Apaches, Hohkams, Hopis, Navajos, and Pueblos were found in Mexico during this time period. They lived in villages, in homes made of adobe, and built irrigation systems to grow corn and other crops. Honoring the earth, the sky, and the water spirits was a big part of the tribes' culture.
Nez Perces, Pomos, and Shoshones, located in California/Great Basin/Plateau, and lived as hunters and gatherers in small family groups. Their diet consisted mainly of fish, berries, and acorns.
Apaches, Arapahos, Blackfeet, Cheyennes, Comanches, Crows, Lakotas, Mandans, and Osagesn were found in the Great Plains. The groups lived in tepees and animals were hunted by men while crops were grown by women. Buffalo was the main source that met basic needs of food, shelter, and clothing.
Apaches, Hohkams, Hopis, Navajos, and Pueblos were found in Mexico during this time period. They lived in villages, in homes made of adobe, and built irrigation systems to grow corn and other crops. Honoring the earth, the sky, and the water spirits was a big part of the tribes' culture.
Nez Perces, Pomos, and Shoshones, located in California/Great Basin/Plateau, and lived as hunters and gatherers in small family groups. Their diet consisted mainly of fish, berries, and acorns.
Apaches, Arapahos, Blackfeet, Cheyennes, Comanches, Crows, Lakotas, Mandans, and Osagesn were found in the Great Plains. The groups lived in tepees and animals were hunted by men while crops were grown by women. Buffalo was the main source that met basic needs of food, shelter, and clothing.
600-1450
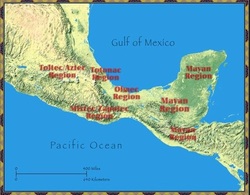
a. The Olmec (1200BCE-300CE)
i. About the Olmecs
1. Located in Saddle of the Yucatan Peninsula
2. First real civilization of south america
3. Teotihuacan center of trade and worship
ii. Interaction Between Humans and the Environment
1. Main area (core)
a. Wet with heavy rainfall
b. Dense tropical forests
c. The first Olmec villages were believed to be non-agricultural because the area where the Olmecs were was a swamp land
i. All these plants and animals could support a small community so people didn’t really have to settle down
d. The Maya lowlands were not affected very much by the Olmecs
e. Their religion is inspired by the environment, and the nature around them.
iii. Development and interaction of cultures
1. Other cultures and societies would help the Olmecs so that they could become bigger
iv. State-building, expansion, and conflict
1. Expansion caused the villages to work together to please the growing population
2. People would often let someones son/daughter marry someone for personal gain, or for alliance between the two families/villages
v. Creation, expansion, and interaction of economic systems
1. The Olmec rulers wanted obsidian, jade, and cacao, this caused them to explore new places, eventually establishing a trade route
a. This also developed lines of communication
vi. Development and transformation of social structures
1. Seperation between elite and commoners.
2. Religion was part of social order
3. Alliance caused by marriages
a. Marriage with Olmec elite could give you a high position in their community
b. The Mayans (300-1500)
i. About the Mayans
1. Largest city Tikal
2. Most of its wealth came from trade
3. Small population
4. They mainly ate maize
5. Had a thing for physical beauty
6. Believed world would be created five times and destroyed four times
7. Most gods were reptilian
ii. Interaction Between Humans and the Environment
1. Would drain and adapt swamps for cultivation
2. They would create reservoirs and waterholes so that they had water during the dry seasons
3. Farmers cleared the rain forests and built raised fields to hold rainwater
iii. Development and interaction of cultures
1. When the Mayan villages would have to work together to produce water for the growing population
2. Highly influenced by the Olmecs
iv. State-building, expansion, and conflict
1. City states flourished from the Yucatan peninsula to Central America
vi. Development and transformation of social structures
1. Each city had its own ruling chief
2. Rulers were usually men
3. Priests held great power
a. They conducted the ceremonies that were needed to ensure good harvests and success in war.
Pyramid of Kukuklan

The Mayan Temples had 365 steps on each side- one step for each day of the year. This particular temple was was the center of a Mayan city built around 700 AD near the southeastern point of Mexico.
Olmec Statue

1450-1750
Aztec Calender

1473-Axayacatl invades Tlatelolco
1519-1524-Cortes leads expedition of Mexico
1521-Tenochtitlan fell to the Spanish invaders
1522-Mexico City was built in the same place as Tenochtitlan and declared as the capital of New Spain
1530-End of Tarasco Empire
1540-1542-Coronado explores area now known as southwest United States
1570-Over 192 Spanish cities and towns throughout the Americas
1570's-much of the Americas is under Iberian control
1740-1800-Population in Mexico increased from 3.5 million to 6 million.
1519-1524-Cortes leads expedition of Mexico
1521-Tenochtitlan fell to the Spanish invaders
1522-Mexico City was built in the same place as Tenochtitlan and declared as the capital of New Spain
1530-End of Tarasco Empire
1540-1542-Coronado explores area now known as southwest United States
1570-Over 192 Spanish cities and towns throughout the Americas
1570's-much of the Americas is under Iberian control
1740-1800-Population in Mexico increased from 3.5 million to 6 million.
2-11-11
Interactions Between Humans and Enviornment
-Aztecs would build canoes,
Development and Interaction of Cultures
-The Aztecs built schools, so that the children would be able to be educated, school was mandatory, boys, girls, and slaves all went
-The Aztecs knew how to cure snake bites, and bone fractures
State-building, Expansion, and Conflict
Creation, Expansion, and Interaction of Economic Systems
-Aztecs would trade with neighbors for materials
Development and Transformation of Social Structures
-
Interactions Between Humans and Enviornment
-Aztecs would build canoes,
Development and Interaction of Cultures
-The Aztecs built schools, so that the children would be able to be educated, school was mandatory, boys, girls, and slaves all went
-The Aztecs knew how to cure snake bites, and bone fractures
State-building, Expansion, and Conflict
Creation, Expansion, and Interaction of Economic Systems
-Aztecs would trade with neighbors for materials
Development and Transformation of Social Structures
-
Analysis
1-27-11
Leader Analysis
Name of Leader: Axayacatl
Title: Aztec Emperor
Country/region: Mexico
Years in power: 1469-1481
Political, social, and economic conditions prior to leader gaining power:
The Aztec empire was rising to its peak of power, they needed a new emperor, and Axayacatl was well suited for the job.
Ideology, motivation, goals:
He wanted to have control of as many other cities as possible.
Significant actions and events during term of power:
He is known for taking control of the city of Tlatelolco.
Short-term effects:
He fought several wars with the Tarascan and lost.
Long-term effects:
He concored Tlatelolco, and made it apart of the Aztec empire.
1-27-11
People Analysis
Name of Group: Mexica aka. Aztecs
Time period: 1300-1520
Location: Central America
Important Neighbors: Tlacopan, Texcoco
Strenghts: Military, Medical
Weaknesses: Had their warriors watch over the farming group of people, telling then what to do, such as slaves, this was one reason for the fall of the Aztec empire.
Impact on neighbors: Conquered most of them, had an alliance with Tlacopan, and Texcoco, this helped establish the Aztecs as a dominant force in Mexico
Legacy: Conquered neighboring cities, towns, societies. They knew how to make medicine for all sorts of things. They lived a legacy of power over others. They also were known for being a nomadic group of people that ended up staying where the future Mexico City (capital of Mexico) would later end up being at.
Leader Analysis
Name of Leader: Axayacatl
Title: Aztec Emperor
Country/region: Mexico
Years in power: 1469-1481
Political, social, and economic conditions prior to leader gaining power:
The Aztec empire was rising to its peak of power, they needed a new emperor, and Axayacatl was well suited for the job.
Ideology, motivation, goals:
He wanted to have control of as many other cities as possible.
Significant actions and events during term of power:
He is known for taking control of the city of Tlatelolco.
Short-term effects:
He fought several wars with the Tarascan and lost.
Long-term effects:
He concored Tlatelolco, and made it apart of the Aztec empire.
1-27-11
People Analysis
Name of Group: Mexica aka. Aztecs
Time period: 1300-1520
Location: Central America
Important Neighbors: Tlacopan, Texcoco
Strenghts: Military, Medical
Weaknesses: Had their warriors watch over the farming group of people, telling then what to do, such as slaves, this was one reason for the fall of the Aztec empire.
Impact on neighbors: Conquered most of them, had an alliance with Tlacopan, and Texcoco, this helped establish the Aztecs as a dominant force in Mexico
Legacy: Conquered neighboring cities, towns, societies. They knew how to make medicine for all sorts of things. They lived a legacy of power over others. They also were known for being a nomadic group of people that ended up staying where the future Mexico City (capital of Mexico) would later end up being at.
1750-1914
1756-1763 Seven Years War
1808-1825 Spanish-American war
1810 Mexican reballion against Spain
1821 Mexico declares Independence
1846-1848 Mexican-American war
1895-1898 United States acquires Puerto Rico and Philippines
1808-1825 Spanish-American war
1810 Mexican reballion against Spain
1821 Mexico declares Independence
1846-1848 Mexican-American war
1895-1898 United States acquires Puerto Rico and Philippines
Analysis
1-27-11
Conflict Analysis
Name of Conflict: Mexico’s War for Independence
Time period: 1810-1825
Type of conflict: War
Underlying causes: Mexican’s wanted equal rights for indians, mestizos, and slaves, they also wanted constitutional rule
Immediate causes: Miguel Hidalgo called for independence from Spain. They did it for social justice.
Turning points/important events: Augustin de Iturbide lead an army to fight against Guerrero’s army in Oaxaca.
Ending events: September 27, 1821 is the day Mexico gained its independence, this was able to happen when rebel forces from all over Mexico joined Iturbide’s army.
End result: Mexico gained its independence
Short-term effects: Many people died. Mexico had to establish itself as an independent country
Long-term effects: Mexico became its own country.
Conflict Analysis
Name of Conflict: Mexico’s War for Independence
Time period: 1810-1825
Type of conflict: War
Underlying causes: Mexican’s wanted equal rights for indians, mestizos, and slaves, they also wanted constitutional rule
Immediate causes: Miguel Hidalgo called for independence from Spain. They did it for social justice.
Turning points/important events: Augustin de Iturbide lead an army to fight against Guerrero’s army in Oaxaca.
Ending events: September 27, 1821 is the day Mexico gained its independence, this was able to happen when rebel forces from all over Mexico joined Iturbide’s army.
End result: Mexico gained its independence
Short-term effects: Many people died. Mexico had to establish itself as an independent country
Long-term effects: Mexico became its own country.
1914 - Present
1968 Tlatelolco massacre